 This two-part blog post focuses on tips for improving your students’ listening skills with both intensive and extensive listening methods. In Part 1, I answer the question “What is intensive listening?”, offer tips for intensive listening practice, and suggest overall listening goals for teachers to bear in mind. After reading Part I, head over to read Listening in Language Learning Part II: Extensive Listening (coming on Monday, July 24th).
This two-part blog post focuses on tips for improving your students’ listening skills with both intensive and extensive listening methods. In Part 1, I answer the question “What is intensive listening?”, offer tips for intensive listening practice, and suggest overall listening goals for teachers to bear in mind. After reading Part I, head over to read Listening in Language Learning Part II: Extensive Listening (coming on Monday, July 24th).
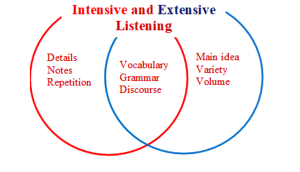
Intensive and Extensive Listening
Much research shows that intensive and extensive listening alike are essential contributors to language learning in the areas of vocabulary development, grammatical skills, and discourse awareness. ESL learners need to practice both skills to reap maximum benefits. Though each form of listening tends to focus on different skills, they are complementary, and both are crucial. However, like extensive reading, extensive listening occurs outside of the classroom. Unlike with intensive listening, teachers need to pay special attention to motivate their students to engage in such extensive skills on their own.
Intensive Listening
Refers to focused and concentrated listening, where learners listen to short audio clips or segments multiple times to understand factual details and suggested meanings in what is being said. This type of listening practice is usually done in a classroom with a teacher. Apart from its listening component, this activity is useful for developing broader language skills such as recognizing specific grammar structures, understanding idiomatic expressions or technical vocabulary, and improving pronunciation.
Teacher Tips for Intensive Listening Practice
Your students can practice their intensive listening skills on a variety of free intensive listening resources. Click here for some free intensive listening practice resources. Teachers should incorporate “guided listening” in the classroom because it can be helpful in directing students to concentrate on grammar and vocabulary. Lyrics Training, for example, provides music videos with exercises, making it great for intensive listening. You can choose between beginner and expert videos.
Above all, it is vital to choose interesting material. As with intensive reading, the teacher is usually the one who chooses intensive listening materials, so, be sure to select materials that are engaging and relevant to your students’ learning goals. When they are interested in the content, they will be more motivated to listen closely.
Learner Tips for Intensive Reading Practice
- Focus on the details: Try listening for specific details like names, dates, and important facts. Pay attention to the main ideas and supporting details. Doing this will help you retain information and understand the content better.
- Listen actively: Focus on identifying the main points, the key details, and the overall message when you listen. Don’t just passively listen without paying attention!
- Repeat and transcribe: Transcribe your interpretation of the material after listening to it multiple times. By doing this, you will build your listening skills and improve your accuracy.
- Practice with a partner: You should practice listening with a partner and ask them to speak slowly and clearly. In case you don’t understand something, you can ask them to repeat or rephrase it. As a result, you will be able to practice your listening skills in a more rewarding and interactive manner.
- Take notes: Take notes while listening to help you remember important details and ideas. If you have a smartphone, you can use a note-taking application. If you would like to know more about notetaking skills, check out my two-part blog on notetaking:
Enhancing Students Notetaking Skills I
Enhancing Students Notetaking Skills II
- Use subtitles: Subtitles are helpful when watching movies or TV shows. This will not only make you feel more confident, but also help you better understand the dialogue and improve your listening comprehension.
- Use different accents: Try to listen to a variety of accents and dialects. This will help you better understand different speakers and improve your overall listening skills.
Coming July 24th, don’t miss Part II – Listening in Language Learning: Extensive Listening to learn more about improving your students’ listening skills!

One could also approach extensive vs intensive in the context of proficiency. Intensive becomes more and more useful for language learners at the intermediate and advances levels I’d say. I’m just thinking out loud here. I am going to be teaching CLB 1 through CLB 3 for my next teaching assignments. Good article!
Do you find intensive listening is more effective at the beginning of their language journey, or after they have some familiarity with the vocabulary, pace, sound, etc?
Reading both articles, intensive and extensive, I would find myself doing intensive after finding a comfort level with the language.