 This two-part blog post focuses on tips for improving your students’ listening skills with both intensive and extensive listening methods. In Part 1, I answer the question “What is intensive listening?”, offer tips for intensive listening practice, and suggest overall listening goals for teachers to bear in mind. After reading Part I, head over to read Listening in Language Learning Part II: Extensive Listening (coming on Monday, July 24th).
This two-part blog post focuses on tips for improving your students’ listening skills with both intensive and extensive listening methods. In Part 1, I answer the question “What is intensive listening?”, offer tips for intensive listening practice, and suggest overall listening goals for teachers to bear in mind. After reading Part I, head over to read Listening in Language Learning Part II: Extensive Listening (coming on Monday, July 24th).
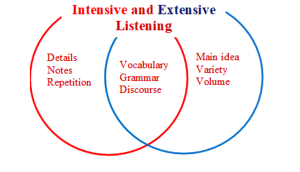
Intensive and Extensive Listening
Much research shows that intensive and extensive listening alike are essential contributors to language learning in the areas of vocabulary development, grammatical skills, and discourse awareness. ESL learners need to practice both skills to reap maximum benefits. Though each form of listening tends to focus on different skills, they are complementary, and both are crucial. However, like extensive reading, extensive listening occurs outside of the classroom. Unlike with intensive listening, teachers need to pay special attention to motivate their students to engage in such extensive skills on their own.
Continue reading →









